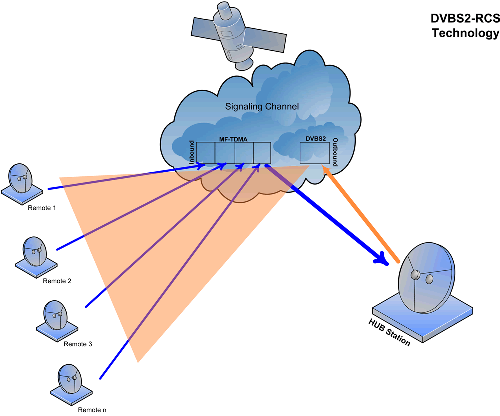
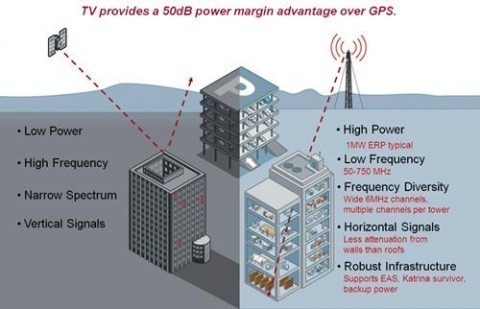
Geostationary Satellite
Geostationary satellites are located exactly above the earth’s equator and revolve around the earth in a circular orbit. Their revolving speed and direction (west to east) are exactly same as that of the earth, which makes it look stationary from the earth’s surface. The exact altitude of these satellites above the equator is approximately 36,000 …