In order to grow a bacterial culture in a lab, a growth medium has to be used to provide the right environment. Mannitol salt agar is a popular bacterial growth medium that biologists use to grow halphile bacteria (these grow fast in high salt concentrations) and can tell the difference between non-pathogenic and pathogenic Staphylococcus (ie parasitic to humans).
Why Are Growth Media Important?
Biologists use growth media in order to raise millions of bacteria in a colony. Some media are liquid – similar to a soup or broth, while others more closely resemble the texture of jello. Besides supporting bacterial growth and sustenance, the media can be used to identify the microbe being studied as well as provide additional information on the organism. Some of the specialized growth media used in research and industry today include MacConkey’s (MAC), Blood agar (BAP), and Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA). Since these media are selective, they not only facilitate the growth of certain types of microbe, but they also prevent undesired bacteria from growing in the media.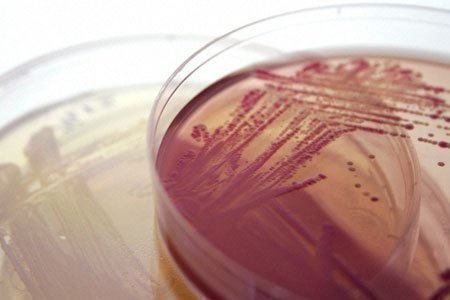
Why Is Mannitol Salt Agar a Selective Media?
Mannitol salt agar has a high concentration of salt or NaCl (7.5 %), which prevents most bacteria from surviving in it. However, staph bacteria (Staphylococcus) prefer a saline or salty medium and grow well in MSA although it will not in others. Mannitol salt is also different from other media in that it contains a dye that identifies different types of Staph that produce organic acids from mannitol fermentation. This waste changes the pH indicator in the media to bright yellow from red. However, pathogenic staph are fermenters, and excrete a bright yellow waste when in a Mannitol salt agar media. Non-pathogenic staph that grows on human skin does not ferment, and will not change the color of the agar.
What is the Typical Composition of Mannitol Salt Agar?
Mannitol salt agar normally consists of the following ingredients:
5.0 g/L enzymatic digest of animal tissue
5.0 g/L enzymatic digest of casein
1.0 g/L beef extract 75.0 g/L sodium chloride
10.0 g/L D-mannitol
15.0 g/L agar
0.025 g/L phenol red
Properly mixed mannitol agar salt will have a pH of 7.4 +/- 0.2 when stored at 25 degrees Centigrade.



Joey
You forgot the salt on that MSA recipe!