Tools for Troubleshooting ISA Server
There are a variety of tools that you can use to troubleshoot ISA Server. The type of issue would determine which of the tools(s) listed here you need to use:
- ISA Server Reports tool: You can use the reporting feature included with ISA Server to obtain and view information on usage statistics of the server for computers and client users, to create your own reports to log specific data, and to isolate the cause of a performance problem. ISA Server includes a number of predefined ISA Server reports:
- Summary reports combine data from the Firewall service log and Web proxy service log, to show network traffic usage.
- Web Usage reports show information on how the Web is being used, and detail information on Top Web users, Common responses, Browsers in use, and Web Usage reports use information in the Web Proxy service logs.
- Application usage reports show information on Internet application usage, and contains information on Amount of incoming traffic, Amount of outgoing traffic, Top users, Client applications, and Destinations.
- Traffic and utilization reports combine data from the Web Proxy logs and Firewall service logs to provide information on Internet usage by application, Internet usage by protocol, Internet usage by direction, Average peaks, Peak simultaneous connections, Cache hit ratio, Errors, and Statistics.
- Security reports combine data from the Web Proxy service logs, Firewall service logs and Packet Filter logs. You can use the information in security reports to monitor for attempts to breach network security, security violations, and network attacks.
To view reports:
- Open ISA Management.
- Expand the Monitoring Configuration node.
- Expand the Reports node.
- Select the report type which you want to view.
- Double-click the report in the details pane.
- Performance Monitor: ISA Server provides the ISA Server Performance Monitor tool to analyze ISA Server performance. The ISA Server Performance Monitor is installed when you install ISA Server. When you access the ISA Server Performance Monitor, the System Monitor node and Performance Logs and Alerts node is displayed. System Monitor uses objects, counters and instances to monitor the system. You can use the ISA Server Performance Monitor to resolve issues on:
- Hardware problems.
- Memory issues.
- Configuration issues.
- Network usage issues.
- Cache performance.
- Event Viewer: An important management tool for administrators of Windows Server 2003 is the Event Log. Event Viewer stores events that are logged in a system log, application log, and security log. You can access Event Viewer from the Administrative Tools folder. Event Viewer can be used to monitor events that took place on a computer. Event Viewer stores events that are logged in a system log, application log, and security log. The system log contains events that are associated with the operating system. The application log stores events that pertain to applications running on the computer. Events that are associated with auditing activities are logged in the security log. This makes Event Viewer a good mechanism to monitor for, and troubleshoot problems. Event Viewer shows all event messages created by the ISA Server services.
The maximum size of the Event Log, Event Log performance, and other attributes are controlled by the following Event Log policies:- Maximum log size; specifies the maximum size for the log file.
- Retain log; sets the time duration for which the Event Log information should be retained.
- Retention method for log; sets what actions should occur when the Event Log’s maximum size is reached:
- Overwrite Events By Days option.
- Overwrite Events As Needed option.
- Do Not Overwrite Events (Clear Log Manually) option.
- Prevent local guests group from accessing log; defines whether the local guests group is allowed to access the Event log.
To open Event Viewer, select Start, Select Administrative Tools, and then select Event Viewer. Simply click the Event log you would like to examine.
- Network Monitor: The tool which you can utilize to both monitor and log network activity as it occurs on the network is the Network Monitor: You can use Network Monitor to monitor network traffic, and to troubleshoot network issues or problems. Network Monitor shipped with Windows Server 2003 and Windows 2000 allow you to monitor network activity and use the gathered information to manage and optimize traffic, identify unnecessary protocols, and to detect problems with network applications and services.
The key administration tasks which you can perform using Network Monitor are summarized below:- You can capture frames directly from the network which you are monitoring.
- You can configure capture filters to specify the type of information which should be captured by Network Monitor.
- You can view captured frames immediately once the capture is complete, or at some later stage.
- You can filter captured frames by creating display filters. This allows you to find specific information in a capture.
- You can create triggers if you want certain actions performed when the content of a packet(s) match a predefined condition.
- You can edit captured frames and pass them on.
- You can capture frames from a remote computer.
You have to install the Network Monitor application and the Network Monitor driver on the server where you are going to run Network Monitor to capture traffic. The Network Monitor driver makes it possible for Network Monitor to receive frames from the network adapter. A frame contains the source address of the machine that transmitted the frame, header information on the protocol that transmitted the frame, the destination address of the receiving machine, and the data sent to the receiving machine. Network Monitor saves captured data to a temporary capture file that you can then save with a .CAP extension. This enables captured data to be examined in Network Monitor. You can design a capture filter to capture only specific frames, or you can configure it to respond to a specific condition.
- Netstat utility: You can use the Netstat utility to troubleshoot security problems and connectivity problems. You can use Netstat utility to:
- Determine the current state of TCP/IP connections.
- View protocol statistical information.
- Obtain information on the following protocols:
- IP.
- TCP.
- UDP.
- ICMP.
- View client mappings, and to determine which process or application is the owner of a particular connection.
Troubleshooting ISA Server Installation Issues
After you have installed ISA Server, you should verify that your installation is operating as expected. You can use the process outlined below as a guideline to verify the ISA Server installation:
- Check the Event log for errors. A few common error messages which you may encounter are listed here:
- Event ID 14111; indicates that the ISA Server cache could not start ue to incorrect configuration. If you cannot resolve this issue, you should run ISA Server setup again and select the Reinstall option.
- Event ID 14010 and14063; indicates that corrupt data in Active Directory or the Registry resulted in the Firewall service not starting.
- Event ID 14164, 14172, and 14176; indicates that an error occurred with disk cache initialization and that the disk cache is disabled. After identifying and correcting the issue, you should restart the Web Proxy service.
- Configure a Web proxy client and ensure that the Web browser application is configured to use the ISA Server.
- Check whether the Internet can be accessed using the Web browser application of the Web proxy client.
- Because the default installation prevents Internet access, you should be returned with the 502 proxy error.
- Create a protocol rule where all ISA Server clients are allowed to use all protocols.
- Then, create a routing rule that routes requests to either of the following:
- Internet.
- Upstream proxy server.
- ISA server.
- Use the client to access the site and verify that the page can be accessed.
Troubleshooting ISA Server Dial-up Connections
The common ISA Server dial-up connection problems, together with recommendations for resolving these issues are discussed here.
- When a Dial-on-Demand Failure event is logged in the event log, it basically means that the connection could not be created. This could possible be due to the line being busy, or because there was no answer. Determine whether any of these issues is the reason for the failure.
- When the Upstream Chaining Credentials event is logged in the event log, you have provided incorrect credentials. Check whether you have entered the valid user provided by the ISP and entered a valid password.
- When the Invalid Dial-On-Demand Credentials event is logged in the event log, it means that the username and password provided of the user is not valid. Check whether you have entered the valid user provided by the ISP and entered a valid password.
- If you receive the 14066 error, it means that the dial-up entry configuration information cannot be read. Check the configuration of the dial-up entry.
- If you receive the 14067 error, it means that the rasapi32.dll failed to load. This is usually due to a system configuration setting that is incorrect.
- If you receive the 14136 error, it means the ISA Server dial-out connection has failed. Try manually dialing the number.
- When only manual dial-out works, and not ISA Server dial-out, check the configuration of the ISA Server dial-up entry and change any incorrect settings. Verify that ISA Server has permission to use the dial-up connection.
- If you receive the 14142 error, it means that dialing out to the Internet has failed. Check your authentication settings and the phone book entry.
- When the ISA server dials out to the Internet when no users have requested connections to the Internet, then active caching is enabled. With active caching ISA Server updates the content in the cache at regular time intervals. If you do not want this to occur, then you have to disable active caching.
- When a dial-up connection is dropped, you can automatically re-establish the connection by restarting ISA Server services.
- When your dial-up server hangs even when no dialing out is taking place:
- Set the ISA Server to use the internal DNS servers.
- Define the DNS server as an ISA Server client.
- Set the DNS server to forward requests that cannot be resolved to an external DNS server.
- If no connections can be established to the Internet through the dial-up connection:
- Check whether the problematic client computer is a SecureNAT client. If it is a SecureNAT client, then you have to install and enable Firewall Client software on the client computer.
- Check whether the dial-up entry has been configured correctly.
- If only manually dialing out to the Internet works, and not automatic dialing out:
- Check whether the problematic client computer is a SecureNAT client. If it is a SecureNAT client, then you have to install and enable Firewall Client software on the client computer
- Check whether the ISA Server computer has the necessary permission to use the dial-up connection.
- Check the configuration of the dial-up entry credentials.
- If the dial-up connection is suddenly dropped:
- Restart the ISA Server services to automatically re-establish the connection.
Troubleshooting ISA Server automatic discovery issues
When troubleshooting ISA Server automatic discovery, consider the following important factors:
- In the ISA Management console, access the ISA Server Properties dialog box and verify the following settings on the Auto Discovery tab:
- The Publish Automatic Discovery Information checkbox should be enabled.
- The correct port should be specified.
- For automatic discovery to work, the ISA Server and the client must have access to either of the following:
- A DHCP server.
- A DNS server.
- A DHCP server and DNS server.
- Check whether the network connection is being established between the client computer, DHCP server, DNS server, and ISA Server computer.
- If you want to use automatic discovery for firewall clients, you have to install and enable the Firewall Client software on the client computer. You also have to enable firewall discovery in the Firewall Client Options dialog box.
- If you want to use automatic discovery for Web Proxy clients, Internet Explorer version 5.0 or above must be used. You also have to configure Internet Explorer to automatically detect settings. This is done in the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings dialog box.
- Check the DHCP server configuration:
- The DHCP server must have the WPAD entry correctly configured.
- Windows NT and Windows 95 clients do not support automatic discovery through DHCP.
- Check the DNS server configuration:
- The DNS server must have a host (A) record that specifies the ISA Server computer.
- The DNS server must also have an alias record for WPAD.
- The alias record should point to the ISA Server computer.
- Verify that the correct port is specified for automatic discovery on the ISA server.
- Verify that the port number in DHCP matches the specified port number.
- Verify that the port number in DNS matches the specified port number.
Troubleshooting ISA client configuration problems
The ISA Server client types are listed here:
- Firewall client: These are client computers on which Firewall Client software is installed and enabled.
- SecureNAT client: These are client computers that have no Firewall Client software installed and enabled.
- Web Proxy client: These are client Web applications which are set up to use the ISA Server computer.
A few common ISA client configuration problems are listed below.
- If yur SecureNAT clients are unable to establish Internet connectivity, the issue is probably incorrect configuration at the SecureNAT clients:
- Check that the default gateway is correctly configured.
- Check that the DNS server is correctly configured.
- If SecureNAT clients can establish connections only when using the IP address and not the computer name, clients might be using an internal DNS server that cannot resolve Internet names: To resolve this issue, you can use either of the following approaches:
- Configure SecureNAT clients to utilize the DNS server which forwards name resolution requests to an external DNS server.
- Configure the DNS server to forward name resolution requests to the external DNS server.
- If SecureNAT clients are unable to connect to a specific port because the connection times out, and you have defined a protocol rule that allows any IP traffic, then the protocol being used is probably not specified in the Protocol Definitions node of ISA Management console:
- For applications that use one port, configure a protocol where that port is the primary port.
- For applications that use more than one port, you have to define these ports through an application filter.
- If clients are unable to access external SSL sites, check which port the client is using to establish a connection to the SSL site.
- ISA Server allows tunnel connections to ports 443 and 563 by default. If you want to specify any other ports, you have to update the ISA Administration COM object – FPCProxyTunnelPortRange.
- If your Firewall clients are experiencing slow internal connections, the issue could be due to clients being unable to resolve local names through an external DNS server.
- To resolve local names, you have to configure an internal DNS server with the names and IP addresses of your internal hosts.
- If packet filtering is enabled, you have to define a packet filter that utilizes DNS Lookup. This will enable the ISA Server computer to forward DNS name resolution queries for Internet names.
Troubleshooting Client Access Problems
The common problems encountered with client access are listed here:
- Client cannot use a particular protocol.
- Clients cannot use the protocol rule specified for the protocol definition.
- Clients are unable to browse external Web sites.
- Clients receive a 502 error whenever they try to browse an external Web site.
- Clients can continue to utilize a protocol when the rule for the specific protocol has since been disabled.
When you install ISA Server in Firewall mode or in Integrated mode, client access is somewhat more increased than when installing ISA Server in Cache mode. When troubleshooting access problems when ISA Server is installed in Firewall mode or in Integrated mode, you typically have to examine the following components to isolate and resolve the issue:
- Protocol rules.
- Packet filters.
- Application filters.
A few common client problems and the strategy which you can use to resolve the issue are summarized here:
- For Firewall clients, check that configuration settings are correct.
- For Web Proxy clients, check whether the Web browser is configured correctly. Determine whether any other site can be accessed.
- Check whether the user is allowed access by a site and content rule. You should check site and content rules applied at the enterprise level and array level.
- Check whether the user is denied access by a site and content rule.
- When authentication is required, check whether the client could process the required authentication.
- Check whether the HTTP re-director filter is enabled for Firewall clients and SecureNAT clients.
When you encounter client access authentication problems, remember the following important factors:
- SecureNAT clients cannot forward user authentication information.
- Firewall clients can forward user authentication information.
- Web Proxy clients that use Internet Explorer can forward user authentication information, but only when configured to forward it.
- To require authentication, enable the Ask Unauthenticated Users for Identification checkbox on the Outgoing Web Requests page of ISA Server properties dialog box.
How to Uninstall ISA Server
- Access ISA Server Setup.
- Select the Install ISA Server option.
- At this point, ISA Server Setup detects all installed files and components and then displays a number of options.
- If you want to add additional components to your current ISA Server installation, then select the Add/Remove option.
- If you want to install any missing files and settings to your existing ISA Server installation, select the Reinstall option.
- If you want to remove ISA Server, select the Remove All option.
- Select the Remove All option.
- When a message is displayed, requiring verification that ISA Server should be uninstalled, click Yes.
- Services are now stopped.
- Click Yes to the message displayed, to verify that you want to remove all logs and backup configuration information created by ISA Server.
- ISA Server Setup now stops the necessary services, removes the ISA Server objects, deletes all necessary files, and then restarts services.

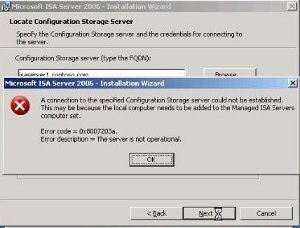
atee
hello all friends 🙄
i have a problem in isa
connectivity active directory is disconnect
can you help me for this problem?