A DSN (Data Source Name) is an identifier that is used to store information relating to a database connection. DSNs can store a database’s name and server location, the directory that is used to store offline content, the database driver, and the user’s ID and password. DSNs can be used for a wide variety of database applications, such as SQL databases and FTP connections.
How DSN Works
A DSN is simply a file that contains all information regarding a particular database. DSNs allow the user to quickly connect to a specific database without having to re-enter its information every time. Like a Notepad document, a DSN stores text-based information, but is also able to automatically fill in the database’s information when the user launches an appropriate database client. While DSNs are usually stored in the Windows Registry, they can also be stored in configurations files belonging to a specific database client that ends in a “.dsn” extension.
Applications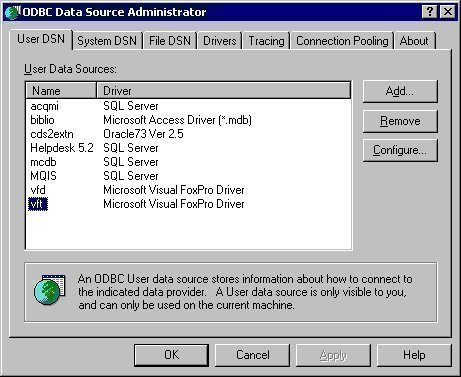
DSNs have a wide variety of applications and can be used on both server-side and client-side programs, but are most often used for the latter. In addition to the user’s information and database’s location, a DSN can also store information relating the database’s permissions and may allow the user to change the database’s permissions by being integrated with the user’s database client. Likewise, the user may be able to change information in a DSN by changing the appropriate factors in the database client.


Follow Us!