The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a series of books that contain proper procedures to handle situations that any IT organization would come in contact with. Using a series of check lists, tasks and procedures, an IT organization can take what is available to it and implement it in such a way that ensures the company’s success. ITIL is broken up into a series of processes.
Service Desk/Service Request Management
The service desk’s responsibility is to handle incidents and requests. It also needs to connect other parts of the service management process. Some of the features of the service desk are single point of contact, single point of entry, single point of exit, and data integrity. It tends to be easier for customers and has a streamlined channel of communication.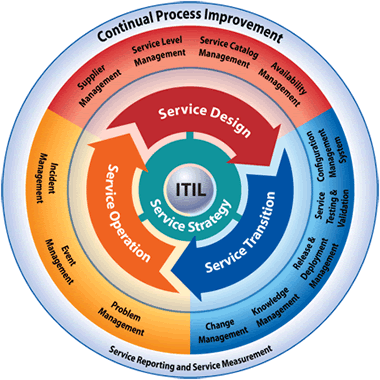
The service desk has two primary functions:
- Incident control – Keeps track of all the service requests and where they are. Currently Communication – keeps the customers informed.
There are a series of names that the service desk can have. They are:
- Call Center: Handles a lot of telephone-based traffic.
- Help desk: Resolves incidents as best as they can.
- Service desk: Handles incidents and connects other departments together.
The service desk is what the customers tend to deal with. While there are deeper layers involved in ITIL, the service desk is the first line of defense and therefore, one of the most important aspects of a successful ITIL implementation.
Incident Management
The incident management’s primary purpose is to restore normal service in a quick fashion that does not have any negative effects on day to day operations. However, one key bit is that service quality and availability are maintained while trying to achieve high recovery speeds.
When anything gets in the way of normal business operations, it is referred to as an incident. This team comes along and does their job to get rid of the incident as quickly and quietly as possible.
Problem Management
While the incident management team works around the clock to try and correct incidents when they appear, the problem management team tries to find the incident’s cause. Therefore, their job is to preemptively get rid of incidents so that customers are not in need of help as often. There are two key words to know when dealing with problem management. They are:
- Problem: A condition that is a result of multiple incidents. All of these incidents exhibit some common symptoms. On the other hand, a problem can also be a single, very large and significant incident.
- Known error: The diagnosis of a problem and the development of a work-around that is a way to get away from the problem.
While both problem management and incident management deal with problems, incident management’s job is to get the service up and running as soon as possible. The problem management’s job is to ensure that any incidents are dealt with and understood.
Change Management
A change is the addition, removal, or modification of configuration items. Change management’s job, therefore, is to handle all of the changes so that there are particular methods to handle them efficiently.
The three main aims of change management are:
- Very little service disruption
- Decrease in any back-out activities
- Utilization of resources involved in change
Release Management
Release management is responsible for ensuring that software and hardware are automatically distributed with the license controls across the IT enterprise. Quality control during installation falls into the hands of release management. The goal is to get the software or hardware installed and implemented into the network as quickly and smoothly as possible so that there are no or few problems. The overall goals of release management are:
- Effective plan of software rollout
- Creating process for distribution and installation of changes
- Management of the customer expectations during the upgrade
- Keeping control of the distribution and installation.
The type of release determines the amount of work that goes into it. There is the major software release that usually has major changes if not entirely new functions. These supersede all other upgrades. The minor software release contains small fixes. It is meant to correct all future problems that were realized. An emergency release is something that corrects a known current problem.
There are also three divides in a release. The first is a delta release that is only part of the software. The second is a full release that is an entirely new version of something. The third is a packaged release that is a combination of a whole plethora of changes.
Configuration Management
As mentioned above, change management is responsible for all addition, modification, or removal of any configuration items. Configuration management has a single process and that is to keep track of all the individual Configuration items in a network.
Service Level Management
Service level management continuously identifies, monitors, and reviews the different levels of the IT services that were specified in the service level agreements (SLAs). It connects internal support providers with external suppliers.
Service level management is responsible for four things:
- Guarantees that IT services that were agreed upon are where they need to be when they are supposed to be there.
- Works together with availability management, capacity management, incident management, and problem management. The goal is to have a certain level of service quality based on the resources that financial management provides.
- Maintains a service catalog, which is a list of options provided to customers.
- Ensures that IT service continuity plans exist for business support.
Capacity Management
The general purpose of capacity management is to allow the organization to do as much as they can with the IT resources that they have. It creates and supports cost effective services. Some of these activities include:
- Application sizing
- Modeling
- Capacity planning
- Performance management
Continuity Management
The overall goal of continuity management is to be proactive about incidents. Instead of reacting to them, continuity management works to reduce the risk of future disaster from occurring. The steps of continuity management are:
- Conduct a business impact analysis to prioritize activities that need to be recovered.
- To identify threats, assets, vulnerabilities, and countermeasures, perform risk analysis for all of the different IT services.
- Consider different recovery options.
- Create a plan.
- Test the plan on a regular basis.
The goal here is to prevent future problems. By having a plan in place, the continuity management can ensure that problems do not hinder the customer.
Availability Management
The general purpose of availability management is to ensure that an organization can sustain its IT needs at a justifiable cost. There are a series of abilities that availability management deals with. They are:
- Reliability: Ability of the component to work at agreed level.
- Maintainability: The components ability to be restored to an operational state if it has not otherwise stayed in that state.
- Serviceability: How well can an external supplier ensure the component’s availability.
- Resilience: It is a method of keeping services reliable. An example of resilience is redundancy. Having a redundant system means that if something fails, there is still a way for it to work.
- · Security: How secure is the system? How secure can the data be?
Availability management ensures that the IT needs are met. Reliability, maintainability, serviceability, resilience, and security are all things that a business needs to keep track of to run efficiently and effectively.
Financial Management
While everything else is going on and trying to create a good system, financial management ensures that it is done within budget. The ultimate goal here is to find the most effective price. The most effective price does not equal cheapest. Instead, it is equal to the best service at the best price. It is financial management’s job to realize the costs of the different services and then ensure that the service’s customer recovers them.


Tin
is ITIL also applicable to IT Asset Management?
Vijay Kumar Reddy
yes, Asset Management also Part of ITIL
Manu
I found your site quite useful and to the point. Information is clearly explained and easy to understand.
Thanks.