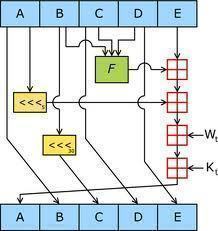
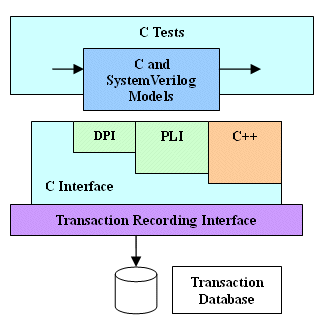
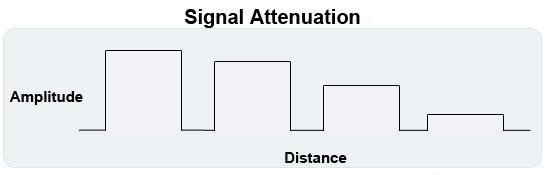
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
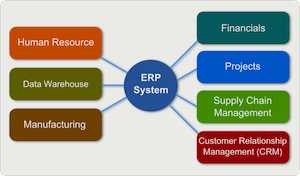
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is principally an integration of business management practices and modern technology. Information Technology (IT) integrates with a corporate house’s core business processes to streamline and accomplish specific business objectives. Consequently, ERP is an amalgamation of three most important components: Business Management Practices, Information Technology, and Specific Business Objectives. In simpler words, …