How Satellite Images Are Made
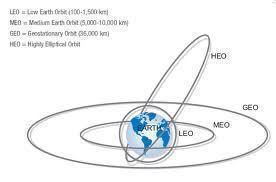
Satellite images are taken by reconnaissance satellites that orbit the Earth at a relatively low altitude, between 300 to 600 miles (or 480 to 970 km). As the majority of today's satellites are custom made in order to accommodate particular needs of the designer, there is no standard on which photo imagery is based on …