Hyper-Threading
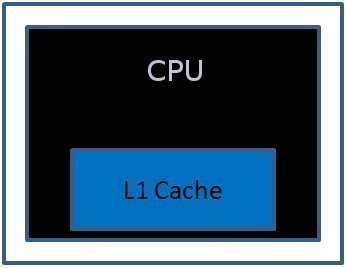
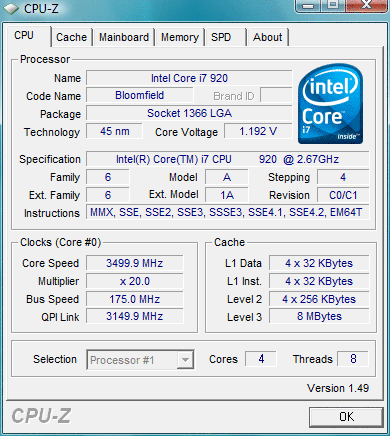
Hyper-Threading technology is a technique that enables a single CPU to act like multiple CPUs. A CPU is made up of many smaller components. At any given time, one of these components might be busy, while the other components are waiting to be utilized. Hyper-Threading enables different CPU parts to work on different tasks concurrently. …