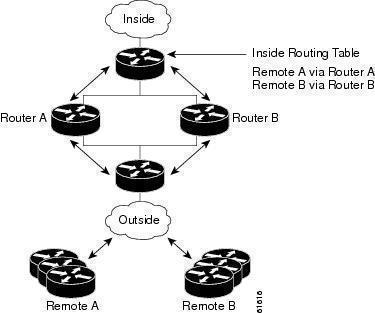
TRIAC
A TRIAC is used in AC power control applications in order to switch high voltages over both parts of the AC waveform. As a result, TRIAC circuits are used in a number of applications that require power switching. The TRIAC was developed after the thyristor, which controls AC current over one half of the cycle. …