Linksys is the home networking division of Cisco, Incorporated and has significant penetration in the U.S. home networking market. A common question that arises for consumers who are new to home or small business networking is determining how to find a Linksys router IP address on a new or legacy network. When shipped from the factory, a Linksys broadband router’s IP address is 192.168.1.1 which is set at the factory. If the end-user needs to change the address due to conflicts with other networking devices on the local or home network, the task can be accomplished via the Linksys router administrative console.
What is the Default Linksys IP Address?
The default IPv4 network or IP address for Linksys broadband routers is 192.168.1.1. The address has become a defacto Linksys standard; however, is defined as a private IP by the IANA ( Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) and can be used by other router manufacturers if desired. As a result, Linksys gives network  administrators the ability to change the Linksys router IP address to avoid network conflicts with other devices that are configured to use the same address (or if you have two Linksys devices on the same network).
administrators the ability to change the Linksys router IP address to avoid network conflicts with other devices that are configured to use the same address (or if you have two Linksys devices on the same network).
What is a Private IP Address?
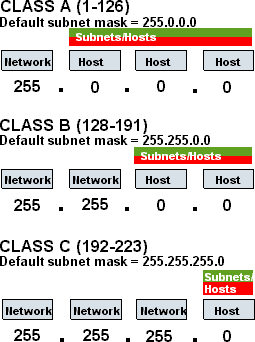
Under the IPv4 IP addressing standard, there are approximately 4.3 billion possible addresses that can be used by networked devices. Although suitable at the time, this limitation has the potential to be a major hurdle for the continued usability of the Internet. To help work around the maximum number of addresses possible, the private IP address ranges defined by the IANA can be used by Linksys and other routers to help share a single IP address across multiple computers on the same network. Private IP addresses are set aside for special reasons with the use in private networking being one of the most popular.
The private IP address ranges are:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
Total IP Addresses: 16,777,216
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
Total: Addresses: 1,048,576
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
Total Addresses: 65,536
How Do Routers Use Private IP Addresses?
There are several tasks that routers use private IP addresses to accomplish. First, is the use of a private IP address such as 192.168.1.1 to allow the end-user to configure or reset the Linksys router. Once configured, the router can share a single network connection with multiple computers on the local network that have private addresses assigned to the computer. Routers accomplish this task by leveraging NAT (Network Address Translation) to change a public IP address to a private one when sending outgoing messages or traffic. Routers that implement NAT are capable of conducting the address translation when sending or receiving network traffic along with the subsequent delivery of the information to one or more devices connected to the local network.
In addition to helping extend the usability of the limited number of IPv4 IP addresses available to Internet users, NAT also performs security and administration functions for networks implementing the protocol. The dynamic NAT implementation results in a firewall being created between the internal network and outside Internet or network. It only allows connections that originate inside of the local domain preventing outside hackers from using a device’s IP and attempting to connect to the port on the computer. Static NAT will allow connections initiated by external computers or devices in specific circumstances only (for example some web server functions). Unlike proxy servers, NAT is transparent to host and client computers working at the same OSI layer as network routers (Layer 3).
What Does DHCP Do?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a service that will assign or lease an IP address and the related information to network clients on the fly (i.e. dynamically). On any network that implements the TCP/IP protocol (most home and small business networks do), each device that connects to the network is required to have a unique IP address and the applicable subnet mask. Without either, the client machine will not be able to successfully communicate. The DHCP protocol handles these assignments automatically without requiring the network administrator to conduct numerous manual entries which can lead to transposition errors. Other default information assigned by the DHCP protocol includes default gateway information, the IP addresses of the required Domain Name System (DNS), and Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) servers. The protocol will ensure that there are no duplicate address assignments made on the network and require no manual intervention on the part of the network administrator or end-user to implement.
How does DHCP work?
DHCP will lease IP addresses on the network for a finite period of time. This prevents the network from running out of address space for client machines that are not always connected or belong to trusted guests or visitors on the network. Before the address is assigned to a client machine; however, the following IP address lease process must occur:
Step 1 – When a client computer that is configured for DHCP connection to a network is being turned on or rebooted, it will send a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast packet out on the wireless or wired network. This data packet will have the computer name and MAC address contained in the data it contains and is required for the DHCP server to conduct its work or lease assignment.
Step 2 – If the packet is received by a DHCP server, the server will then respond to the message with a DHCPOFFER broadcast. This message lets the client computer know that it has an available address. It is possible for client computers to receive multiple offer data packets. If this occurs, the computer or device will accept the first offer received.
Step 3 – The client device will now send a response to the DHCP server called the DHCPREQUEST. The intention of this message is to inform the server that the offer of an IP address has been accepted. If there is no message received in response to an address offer by a DHCP server, the request will be rescinded.
Step 4 – The DHCP server that receives the IP address offer acknowledgement will then send a DHCPACK message. This message acknowledges the lease acceptance and will contain the IP address being assigned and the other information required to use the network. At this point, the client computer or device is now considered a full TCP/IP client.
What Are the Methods of DHCP Address Allocation?
DHCP servers can assign IP addresses in one of three ways: dynamically, automatically, or through static assignment. The dynamic allocation of addresses occurs when a computer administrator assigns an IP address range to the DHCP server. Each client device on the network is required to request an IP from the server when the network is initialized. Once an IP address lease expires, the DHCP server can reclaim the address if it is not renewed for future assignment or use. The automatic allocation of address occurs when a DHCP server is setup to permanently assign a free IP from a range set by the administrator to the requesting device. The server will keep a record of past assignments and attempt to assign the same IP to the same device on future address requests. Static IP allocation occurs when the DHCP server is configured to assign addresses based on MAC address and IP pairings. If a MAC address is not stored on the server, the requesting computer will not receive an address assignment.
What Are the DHCP Security Vulnerabilities?
DHCP was not designed to include security mechanism in the baseline protocol definition for authentication purposes. As a result, there are several well-known network attacks that take advantage of the lack of authenticating procedures with the protocol:
Vulnerability #1 – Unauthorized computers can potentially gain access to the network or its resources.
Vulnerability #2 – Rogue network computers can exhaust network resources.
Vulnerability #3 – Unauthorized DHCP servers can be introduced that provide false assignments to client computer.
At the time of this writing, there are several extensions to the DHCP standard that implement various authentication schemes; however, none of them are widely used throughout industry. The primary means that network administrators use to work around these issues is to control the access to the network itself.
When Was DHCP Invented?
The first definition of DHCP was in RFC 1531 in October of 1993. This definition defined the protocol as an extension of the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP). BOOTP had been found to have a number of short comings to include manual action to add client configuration information and no means to automatically reclaim abandoned or disused IP addresses. As DHCP gained popularity, it was further refined through RFC 2131 that was released in 1997. The DHCP protocol has been redefined for use in IPv6 networks in RFCs 3315, 3633, and 3736 and include stateless address auto configuration.
How Do You Change the Linksys Router IP Address?
If two or more Linksys routers are going to be used on the same network, the IP address for one of the routers will need to be changed. The IP address for a Linksys router can be changed using the router administrator console.
Step 1 – Ensure the Linksys router is turned on and connect your computer to the router using an Ethernet cable.
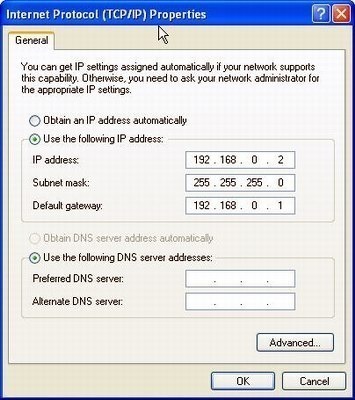
Step 2 – Launch the web browser on the computer and enter the default IP address for the router in the browser address bar, 192.168.1.1.
Step 3 – Open your web browser. Enter the IP address for your Linksys in text box. The default IP address for your Linksys is 192.168.1.1.
Step 4 – Enter the login name and password on the router login screen that appears on your computer’s web browser. If the login and password have not been changed since purchase, the default login name will be blank with a password of “admin.”
Step 5 – Choose the “Setup” menu option located at the top of the console screen. This menu option will contain all of the main configuration settings for the Linksys device to include the IP address settings.
Step 6– Input a new IP address in the text box labeled “Local IP Address.” The local address will need to be in one of the private IP address ranges or the router will likely fail to work properly.
Step 7 – select the “Save Settings” menu button. If the router does not automatically reboot, manually force it to do so.
Step 8 – After the router has rebooted, enter the new IP address in the browser address bar to verify that it works.
How to Obtain a New IP Address on a Linksys Router
Step 1 – Connect your computer to the Linksys router using an Ethernet cable connected to any of the LAN ports on the rear or back of the router. Ensure that you avoid plugging the cable into the uplink port that is located next to the power source. After successfully connecting the computer to the router with both machines turned on, lights will begin turning on the computer port that the cable is plugged. If you see no lights, then there may be issues with the Ethernet cable.
Step 2 – Enter the default Linksys IP address (192.168.1.1) in the web browser’s address bar followed by clicking the “enter” or “return” key on your computer’s keyboard. Once the login screen appears, enter the username and password for the router if you have changed these since installing the device. If they have not been changed, then enter “admin” for the password and leave the username blank.
Step 3 – Record all ISP network settings located under the “Setup” menu for the router. Some Internet Service Providers will require the domain or hostname to be entered under the DNS settings option. Once the router is connected to your ISP, it then serves as a local DHCP server for client devices on the home or work network.
Step 4 – Select the “Release and Renew” menu button to get a new IP address from the ISP assigned to the router. This will normally happen automatically when connecting the router to the cable or DSL modem as the majority of broadband ISPs use DHCP for customer IP address assignments. When using a DSL connection, the appropriate PPPoE settings must be selected.
Step 5 – Plug the WAN port into the router from the modem and the router will automatically be assigned an external IP address from the ISP. If you select the DHCP Release and Renew menu options on the status page, the router will request a new IP again from the ISP’s DHCP server.

Value Host
I think what you posted made a bunch of sense. But, think on
this, suppose you wrote a catchier post title?
I ain’t saying your content isn’t good, but what if you added a post title that grabbed a person’s attention? I mean How to Find a LinkSys Router IP is kinda boring. You might peek at Yahoo’s home page and
watch how they create news titles to grab people to open the links.
You might try adding a video or a pic or two to get people interested about
everything’ve written. Just my opinion, it could bring your website a little bit more interesting.
Blahvlah
Connecting your computer to the router and then booting will NOT cause the router’s configuration to be displayed on the screen.
Marlon Franco
yup, you still need to manually go to the router’s configuration screen. See the instructions above.
Shawn
We changed our IP address a while back, and now we can’t remember it. Is there a way I can recover it?
memenode
To find your current IP address you can just go to: WhatIsMyIPAddress.com
SC
have wildblue sat internet, trying to change to quest, cannot get a connect to 192.168.0.1 get have a tech error contact provider..blah blah. this is the second modem I have tried..first one I was told was bad, sooo here I am after exchanging and still same problem.. any ideas?? perhaps something with setup that I am missing. have just enough skills to be dangerous not intelligent.
memenode
Shouldn’t the address be 192.168.1.1?
Eddy
Canot Connect 192.168.1.1. i dont know how to connect to my router. Pls Help me
alice shrewsberry
I use a router to connect my laptop to a sattelite (hughes net) I purchased a wireless printer my computer recognizes the printer but will not print
memenode
If it recognizes it then it should be able to print. Make sure it is turned on, and there is paper in the tray.
What does it tell you when it wont print?
jdf
I still can’t change my password or user name. 😳
Barb Davis
I have a wireless router and the home computer connects to internet as well as a laptop, but cannot connect to the internet on my IPod Touch