A routing protocol is the implementation of a routing algorithm in software or hardware.
A routing protocol uses metrics to determine which path to utilize to transmit a packet across an internetwork.
The metrics that routing protocols use include:
- Number of network layer devices along the path (hop count)
- Bandwidth
- Delay
- Load
- MTU
- Cost
Routing protocols store the results of these metrics in a routing table.
A router connects different networks with each other to share packets of data. To route a packet, a router needs to know:
- Destination IP addresses
- Learning sources
- Possible routes to the destination
- Best route to the destination
- Verify and maintain the routing information
Routers must learn the destinations that are not directly connected through IP routing. Routing uses a route that a network routing protocol adjusts automatically for topology or traffic changes. Routing protocols are used between routers to determine paths and maintain routing table. Once the path is determined a router can route a routed protocol such as IP while RIP, the Routing Information Protocol is an example of routing protocol.
The other examples of routing protocols are as follows:
- BGP: Border Gateway Protocol
- EGP: Exterior Gateway Protocol
- EIGRP: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
- IGRP: Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
- IS-IS: ISO IS-IS
- OSPF: Open Shortest Path First
There are three classes of routing protocol:
- Distance Vector Routing Protocol such as RIP and IGRP
- Link State Routing Protocol such as OSPF
- Hybrid Routing Protocol such as EIGRP
Interior vs. Exterior Routing Protocols
Some routing protocols are designed to be used within an organization, while other routing protocols are designed for use between organizations.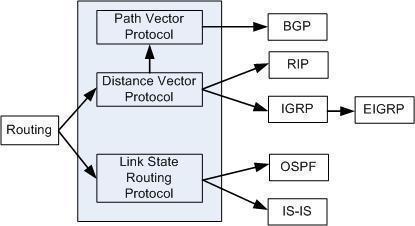
The current lead Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) is OSPF. Other Interior Gateway Protocols include IS-IS, RIP, and EIGRP.
The current lead Exterior Gateway Protocol is BGP. The current revision of BGP is BGP4. There are no other Exterior Gateway Routing protocols in current competition with BGP4.
Distance Vector vs. Link State Routing Protocols
Routing protocols such as RIP and EIGRP are Distance Vector routing protocols. These are called Distance Vector protocols because they base routing decisions on the “distance” of the remote destination in terms of the number of network layer hops that the packet will have to traverse.
OSPF and IS-IS are Link State routing protocols. They are called Link State protocols because they base routing decisions on messages received from other routers in the internetwork that give information about the state of the links connected to them.
Information on RIP, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP Routing Protocol
The Routing Information Protocol is an open standard based Distance-Vector routing protocol. It comes on two versions RIP v.1 and RIP v.2.
The Open Shortest Path First is an example of Link State routing protocol that supports variable length subnet masking and discontiguous subnets.
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol is an enhanced Distance Vector routing protocol. It is also known as hybrid routing protocols that shares the attributes of both Distance Vector and Link State. It is a scalable routing protocol, even the largest EIGRP installation in the world network is running successfully with no EIGRP offset.
The Border Gateway Protocol is an exterior gateway protocol that provides inter-autonomous system routing. It is the protocol of the internet. BGP operates in one of two modes: internal BGP and external BGP.

jakes
given a network and you are trying to configure a router,which routing protocol would you use and where would you use it?
radha
not yet clear informatation in Ur site plz confrome the what he ask the give answer