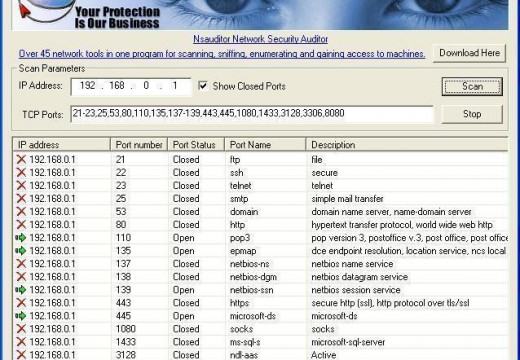
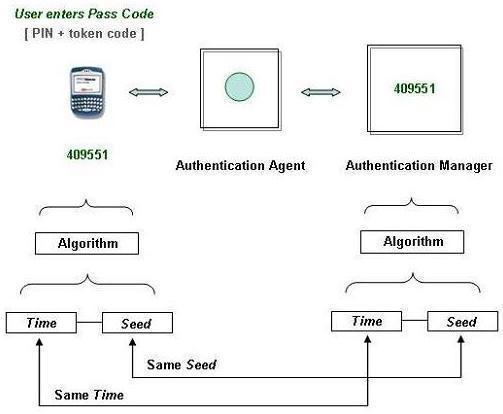
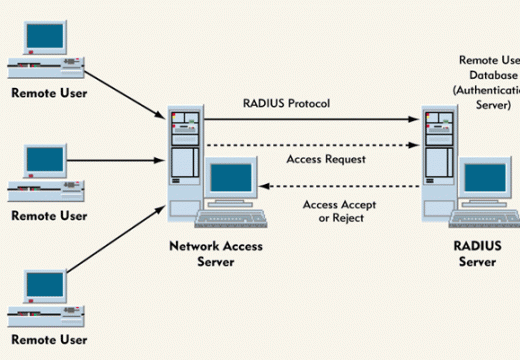
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
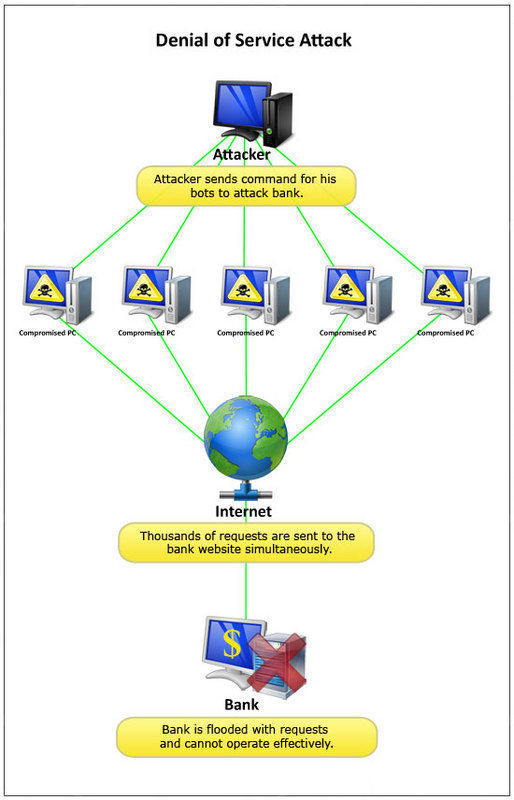
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack is one that attempts to prevent the victim from being able to use all or part of his/her network connection. A denial of service attack may target a user to prevent him/her from making outgoing connections on the network. It may also target an entire organization to either prevent …