MOLAP
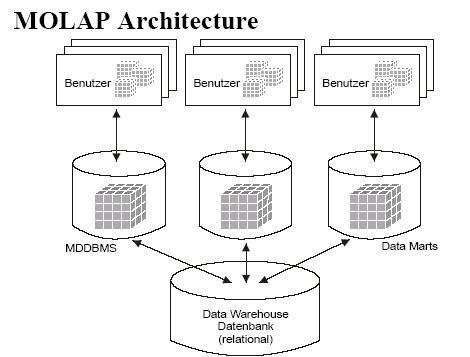
MOLAP is the term used to refer to multidimensional online analytical processing. It extends traditional OLAP processing through indexing directly into a multidimensional database. This allows users to view various data aggregates in different manners without the added overhead required to conduct similar operations with a relational database. Advantages and Disadvantages of MOLAP Some of …