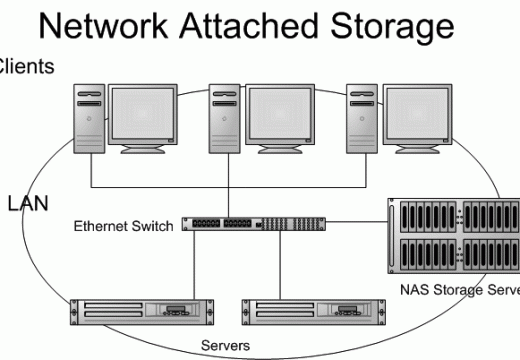
Network Attached Storage
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is a term used to describe a complete storage system which is designed to be attached to a traditional data network. This differentiates Network Attached Storage devices from SAN's (Storage Area Networks). A SAN is a separate network to which storage devices are attached. In most cases, Network Attached Storage is …