HRTF (Head Related Transfer Function)
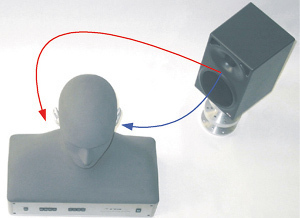
HRTF (Head Related Transfer Functions) refers to a technique used in audio recordings in order to produce binaural signals from a monaural source. While monaural signals refer to sounds that a signal source produces and both ears hear them at varying distances and frequencies, binaural signals refer to sounds that two separate sources produce and that each ear …