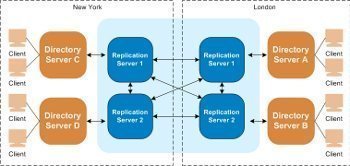
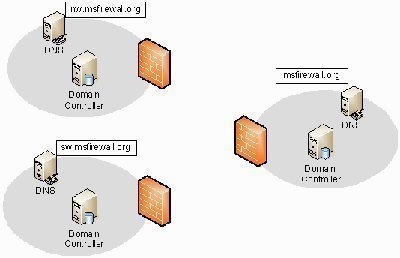
Replication Topology in Active Directory
Replication Topology is the route by which replication data travels throughout a network. Replication occurs between two domain controllers at a time. Over time, replication synchronizes information in Active Directory for an entire forest of domain controllers. To create a replication topology active directory must determine which domain controller's replicate data with other domain controllers. …