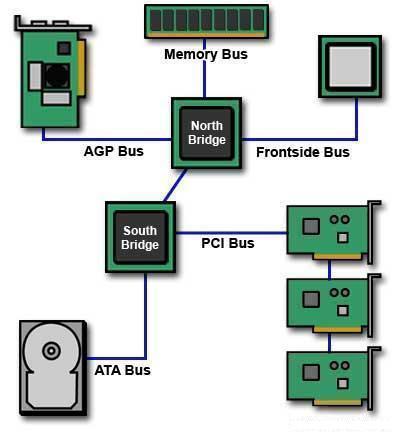
CPU Speed
CPU speed is not a good indicator of CPU performance. Many factors inside and outside of the CPU significantly impact the CPU and overall system performance. The CPU “CPU” stands for Central Processing Unit, and is also known as a “processor”. The CPU speed, or processor speed, is the amount of cycles that a CPU …