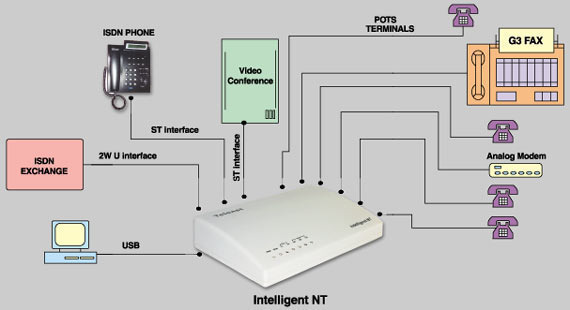
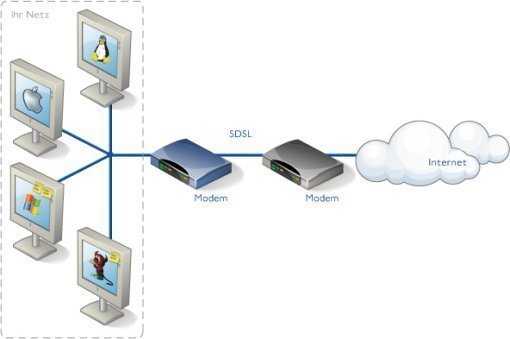
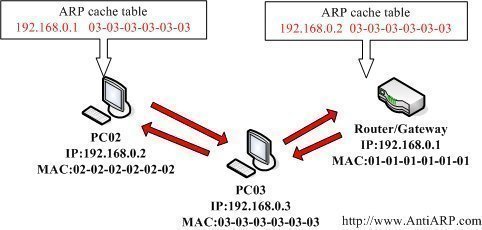
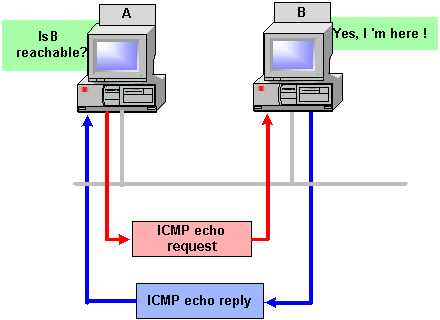
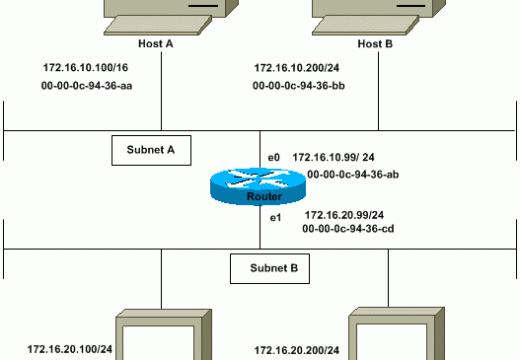
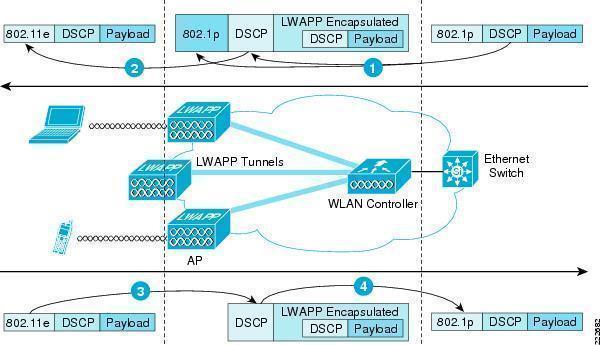
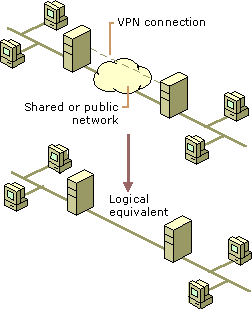
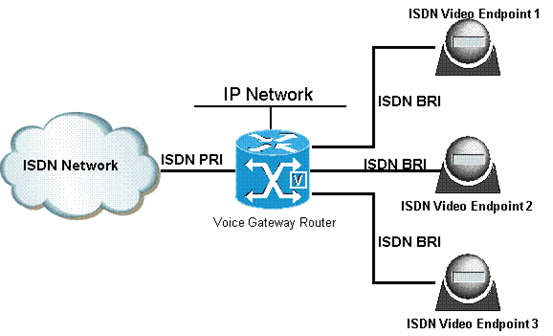
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network)
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) is a system of digital phone connections that has been designed for sending voice, video, and data simultaneously over digital or ordinary phone lines, with a much faster speed and higher quality than an analog system can provide. ISDN is basically a set of protocol for making and breaking circuit …