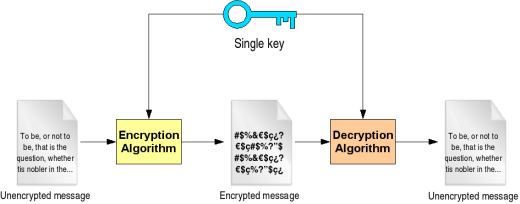
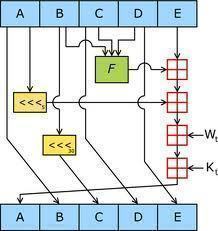
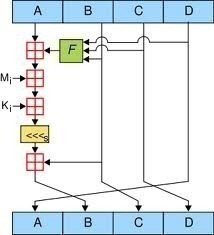
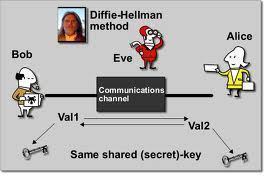
Cryptanalysis
Cryptanalysis is the study of analyzing information systems in order to “discover” or “crack” the hidden or secret aspects of those systems. More specifically, cryptanalysis is the study of breaching cryptographic security systems in order to obtain access to the information contained within encrypted messages without necessarily knowing the cryptographic key used to encrypt the …