The Domain is the core unit of logical structure in Active Directory. All objects that share a common directory database and trust relationship with other domain and security policies are known as Domains. Each domain stores information only about the objects that belong to that domain.
All security polices and settings, such as administrative rights, security policies, and Access Control Lists (ACLs), do not cross from one domain to another. Thus, a domain administrator has full rights to set policies only within domain they belong to.
Domains provide administrative boundaries for objects and manage security for shared resources and a replication unit for objects.
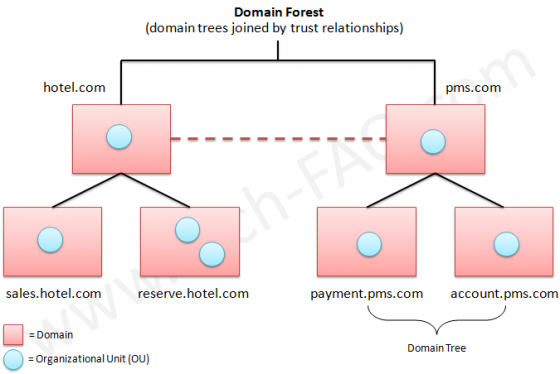
A Tree
Trees are collections of one or more domains that allow global resource sharing. A tree may consist of a single domain or multiple domains in a contiguous namespace. A domain added to a tree becomes a child of the tree root domain. The domain to which a child domain is attached is called a parent domain. A child domain can also have its multiple child domains. Child domain uses the name then its parent domain name and gets a unique Domain Name System (DNS).
For example, if tech.com is the root domain, users can create one or more Child domains to tech.com such as north.tech.com and or south.tech.com. These “children” may also have child domains created under them, such as sales.north.tech.com.
The domains in a tree have two way, Kerberos transitive trust relationships. A Kerberos transitive trust simply means that if Domain A trusts Domain B and Domain B trusts Domain C, then Domain A trusts Domain C. Therefore, a domain joining a tree immediately has trust relationships established with every domain in the tree.
A Forest
A forest is a collection of multiple trees that share a common global catalog, directory schema, logical structure, and directory configuration. Forest has automatic two way transitive trust relationships. The very first domain created in the forest is called the forest root domain.
Forests allow organizations to group their divisions that use different naming schemes and may need to operate independently. But as an organization, they want to communicate with the entire organization via transitive trusts and share the same schema and configuration container.

Mohammad Shaikh
super explanation of Domain, tree, and forest really really thank you for this content it will helps me soo much
calip
Thanks a lot !!, I didn’t understand this concept even after going through technet and wikipedia
Abdulqader Kapadia
Sorry for the inconvenience. We have replaced the image with a cleaner and legible diagram.
Web User
Nice – disable right-clicking so the diagram of the forests and trees can’t be opened in another window where it might actually be legible. Well done.
Web User
My bad – http://www.tech-faq.com/wp-content/uploads/images/tree-and-forest-in-active-directory.jpg isn’t legible, even if viewed in another window. Keep it useful.
Will Spencer
Right-Clicking works fine for me.
saikumar
Its clearly understandable…. superb.
shailesh
it is very good understandable, pls add example
Abhinav
very well explained…
sandeep
thanks a lot sir for given me such a great informatin……………..
Palash Bhattacharyya
Thanks it is very clear and understandable, But i would have appreciate if u could expain along with some example and diagram
Thanks & Regards
Palash (Desktop Engineer)
Rijvana
Thank you so much for giving very useful information.
Rijvana
anilk
great yaar. you made me understand.Thanking you.
vishu noty
got my ans thnks mate 🙂
manu
oh! ts great nd informative nw m confident tht i can gear to my next exams .. 🙂
Chandra Bose Sharma
great yaar. you made me understand.Thanking you.
Abuga
nice explanation made me understand Tree and Forest.thanks for this
Bala
Grt information and its vry useful. Thnks a lot
Joel
Tree & Forest Defenision Very good, pl add Examples…
Srikant
Hi…its very nice way of explaining the structure, however would be muh appreciated if the tree and forest architecture is explained and the scenario where it can be used would help us to improve our concepts..Anywayz thanks for such a useful post…Wouls like to see some more in future
Thanks
Srikant
mehedi
fantastic article but missing some example in the forest description……