Active Directory is a distributed multimaster replicated database. All domain controllers host a full replica of the domain information for its own domain. Domain controllers in Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 environments hold a read/write copy of the Active Directory database. In these environments, changes can be made to the Active Directory database on any domain controller within the Active Directory environment. Replication is the process that ensures that changes made to a replica on one domain controller are transferred to replicas on the remainder of the domain controllers. When an object in Active Directory is created, deleted, moved, or changed Active Directory replication is triggered.
In Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 environments, the types of Active Directory replication that can be defined are:
- Intrasite Replication: Intrasite replication takes place between domain controllers within the same site. This makes intrasite replication an uncomplicated process. Intrasite replication utilizes the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol to convey replication data over fast, reliable network connections. Replication data within a site is not compressed.
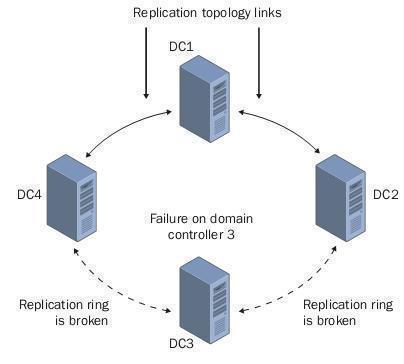
- Intersite Replication: Intersite replication takes place between sites. Intersite replication can utilize either RPC over IP or SMTP to convey replication data. Intersite replication has to be manually configured. Intersite replication occurs between two domain controllers that are called bridgeheads or bridgehead servers. With intersite replication, packets are compressed to conserve bandwidth.
The information replicated in Active Directory is summarized below:
- Configuration partition data: Objects stored in the configuration partition relate to the domain structure and replication topology and are replicated to each domain controller in each domain and in a forest.
- Domain partition data: All objects that are stored in a domain exist in the domain partition. Domain partition data is replicated to the domain controllers within a domain.
- Schema partition data: Schema partition data include information on the objects that can be created in Active Directory and is replicated to each domain controller in domains/forests.
- Application partition data: A new feature introduced in Windows Server 2003 is the application partition. Applications and services store data in the application partition.
Users can use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to configure intersite replication. Configuring intersite replication typically involves:
- Renaming the Default-First-Site-Name object
- Creating site objects and subnet objects
- Creating site link objects
- Configuring site link attributes: Site link cost, site link replication frequency, site link replication availability
- Specifying or designating a preferred bridgehead server (BS).
- Creating site link bridges
- Manually creating connection objects
How to Rename the Default-First-Site-Name Site (first site object)
It is a good idea to rename the default site object to something that has meaning in the organization. To do this:
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Right click Default-First-Site-Name and select Rename from the shortcut menu.
- Proceed to set a meaningful name for the site.
How to Create a New Site Object
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Right click the Sites folder and select New Site from the shortcut menu.
- When The New Object – Site dialog box opens, enter a name for the site in the Name box.
- Users can accept DefaultIPSiteLink in the Link Name box.
- Click OK.
How to Create a New Subnet Object
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Right click the Subnets folder and select New Subnet from the shortcut menu.
- When The New Object – Subnet dialog box opens, in the first section of the dialog box, specify the subnet address and the number of bits in the subnet mask.
- In the Select a site object for this subnet section, specify the site object with which this particular subnet is associated.
- Click OK.
How to Create a Site Link
When users create a site link they can specify the transport protocol for replicating data over site links as either IP or SMTP.
- IP replication is typically selected for a site link when a reliable connection exists between domain controllers in different sites.
- SMTP replication is normally selected when connections are unreliable and slow.
To create a site link:
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Open the Sites folder then open the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Right click either the IP folder or the SMTP folder and choose New Site Link from the shortcut menu.
- The New Object-Site Link dialog box opens.
- In the Name field, enter a name for the new site link.
- In the Sites Not In This Site Link box, select the sites to connect. Click Add.
- Click OK.
How to Configure Site Link Attributes or Properties
Configuring site link attributes involves specifying site link costs, the site link replication frequency, and setting site link replication availability. When users set the site link cost, they are basically defining the cost of the network connection proportionate to the speed of the link. Lower costs are utilized for fast links, while higher costs are associated with slower links. The site link replication frequency can be a number ranging from 15 minutes to 10,080 minutes. Setting site link replication availability involves specifying when a site link is available for replication.
To configure site link attributes:
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Open the Sites folder then open the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Open the IP folder or SMTP folder that contains the site link for which attributes should be configured.
- Right click the particular site link then select Properties from the shortcut menu.
- In the Description box in the General tab of the Properties dialog box for the site, enter a description for the site link.
- In the Cost box, change the default cost for the site link and assign a cost to the link. The default cost setting is 100.
- In the Replicate Every box, change the default replication interval. This is basically the number of minutes between replications. The default setting is 180 minutes. The shortest replication interval that can be set is 15 minutes and the longest interval that can be specified is 10,080 minutes.
- Click the Change Schedule button to configure when the site link is available for replication.
- When the Schedule dialog box for the site link opens, set when the site link is available for replication or when it is not available for replication.
- Click OK to save configuration changes made in the Schedule dialog box.
- Click OK to save changes in the site’s Properties dialog box.
How to Configure Replication to Disregard/Ignore Schedules
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Open the Sites folder, then open the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Right click the IP folder or SMTP folder and choose Properties from the shortcut menu.
- When the Properties dialog box of the folder selected opens, click the Ignore Schedules checkbox.
- Click OK.
How to Add a Site to an Existing Site Link
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Open the Sites folder then open the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Open the IP folder or SMTP folder that contains the site link to which the site should be added.
- Right click the particular site link then select Properties from the shortcut menu.
- Use the Sites Not In This Site Link box to select the site that should be added to the site link. Click Add.
- Click OK.
How to Rename an Existing Site Link
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console
- Open the Sites folder then open the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Open the IP folder or SMTP folder that contains the site link to be renamed.
- Right click the particular site link and select Rename from the shortcut menu.
- Set a new name for the site link.
How to Designate a Preferred Bridgehead Server (BS)
The Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) could possibly not designate a bridgehead server that is the most optimal domain controller in a site. In cases like this, manually designate a preferred bridgehead server(s) to improve performance.
To designate a preferred BS:
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- In the console tree, expand the Sites folder, expand the site to create the bridgehead server in, then expand the Servers folder.
- Right click the particular server and select Properties from the shortcut menu.
- When the server’s Properties dialog box opens, in the Transports available for inter-site transfer section, select the protocol for which the server is to be a bridgehead server. Click Add.
- Click OK.
How to Disable Transitive Site Links or Automatic Bridging
Because site link transitivity is enabled by default, users typically need to disable in order to create site link bridges.
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Open the Sites folder then open the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Right click either the IP folder or SMTP folder and choose Properties from the shortcut menu.
- On the General tab, uncheck the Bridge All Site Links checkbox to disable site link transitivity.
- Click OK.
How to Create a Site Link Bridge
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- Open the Sites folder then open the Inter-Site Transports folder.
- Right click either the IP folder or SMTP folder and choose New Site Link Bridge from the shortcut menu.
- The New Object-Site Link Bridge dialog box opens.
- Enter a name for the new site link bridge in the Name field.
- Use the Site links not in this bridge box to select two or more sites to connect. Click Add.
- Click OK.
How to Manually Create and Configure a Connection Object
The KCC Automatically creates connection objects in Active Directory. However, users can manually create connection objects to customize the network’s topology or decrease the number of hops from one domain controller to another particular domain controller. When the KCC creates connection objects, the KCC automatically removes them when the replication topology changes. Connection objects that are manually created are not removed when the replication topology changes. Users have to manually remove these connection objects.
To manually create and configure connection objects:
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- In the console tree, expand the Sites folder, expand the site in which the connection object will be created, then expand the Servers folder.
- Select the particular server for which the connection should be enabled.
- Right click NTDS Settings and select New Active Directory Connection from the shortcut menu.
- When the Find Domain Controllers dialog box opens, choose the domain controller. Click OK.
- When the New Object-Connection dialog box opens, enter a name for the connection object. Click OK.
- Right click the connection just created in the details pane and select Properties from the shortcut menu.
- When the connection object’s Properties dialog box opens, provide a description for the new connection object in the Description field.
- In the Transport drop down list, verify that RPC is specified as the transport protocol.
- To modify the default schedule for intrasite replication, click the Change Schedule button.
- When the Schedule dialog box for the connection object opens, set the appropriate replication frequency and Click OK.
- Click OK to save changes made in the connection object’s Properties dialog box.
How to Manually Force Immediate Replication
- Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
- In the console tree, expand the Sites folder, the site that Active Directory has to replicate to, and expand the name of the server to use for replication.
- Click NTDS Settings to display the server’s inbound connection objects in the right pane.
- Right click the server to be replicated from and click Replicate Now from the shortcut menu.
Troubleshooting Active Directory Replication
Although domain controllers automatically manage the replication process, there are instances when incorrect configuration settings or troublesome network connections can prevent Active Directory information from being replicated between domain controllers. There are quite a few mechanisms that can be used to monitor and troubleshoot the Active Directory replication process.
The tools available are:
- Active Directory Replication Monitor (Replmon.exe).
- Replication Diagnostics Tool (Repadmin.exe).
- The Dsastat.exe command line tool.
- Users can also configure Active Directory event logging.
A few common methods that monitor or troubleshoot Active Directory replication are summarized below:
- Verify network connectivity in one’s environment: When Active Directory replication has stopped, verify the existing network connections. For replication to occur, capable LAN links have to connect the domain controllers. Using high speed links typically improves replication performance.
- Verify site links: In order for domain controllers in different sites to exchange Active Directory data or information, users have to configure the appropriate site links. When replication is not occurring between sites, verify that a site link object does link the current site to a site that is connected to the remainder of the sites of the network.
- Verify the replication topology: Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to check whether the replication topology is reliable and constant. Errors are displayed in a dialog box in the console.
- Manually verify that Active Directory information has been synchronized. Verify that information is synchronized between domain controllers within domains on a regular basis.
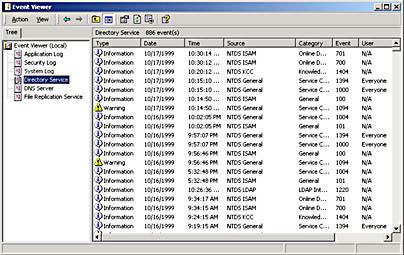
- When replication errors are encountered, check the Directory Service event log in Event Viewer. Active Directory replication errors are written to the Directory Service event log.
There may be instances when Active Directory replication is quite slow. A few methods of correcting this problem are summarized below:
- Having no site link bridge can result in Active Directory information taking quite a while to be replicated between domain controllers. Users can create a site link bridge or can bridge all sites. This is typically necessary when there are only site links in the network, but no site link bridges.
- If the configuration value specified for the frequency of intersite replication is set too low, users may experience large delays between when changes are made on one domain controller and when they are replicated on a domain controller in a different site. To fix this problem, consider changing the replication frequency’s setting.
- When the existing network resources are unable to cope with the quantity of traffic that Active Directory replication generates, consider the following:
- If realistic, modify the replication frequency’s setting.
- If feasible, configure additional resources for Active Directory replication.
- Create site links.
- Create site link bridges.
How to use Active Directory Replication Monitor to Monitor/Troubleshoot Replication
Replication Monitor (Replmon) is a graphical management tool included in the Windows Support Tools. In order to open and use Replmon, it must be installed on a computer. The computer can be a domain controller, member server, member workstation, or stand alone computer. Replication Monitor can be used to perform the following activities:
- View the replication topology or replication information in a highly useful graphical format.
- Determine whether domain controllers are replicating Active Directory information correctly.
- Determine Active Directory replication’s status.
- Manually force replication between domain controllers.
The information displayed in the main Replication Monitor window is listed below:
- Naming contexts: All the naming contexts that a server contains are displayed here.
- Replication partners: Each naming context shows the inbound replication partners for that particular naming context.
- Server icons: Server icons enable users to determine information at a glance.
- Log entries: The replication log entries for the connection are displayed in the right pane.
Once a domain controller for monitoring is specified, set view options to suit on’es needs. To specify view options, open Replication Monitor and select Options from the View menu. The options that can be selected on the General tab are:
- Show Retired Replication Partners.
- Show Transitive Replication Partners and Extended Data.
- Notify When Replication Fails After This Number Of Attempts.
- Log Files: Settings under Log Files are used to change the default location for the log files.
- Enable Debug Logging: This setting relates to debugging Replmon.
The Replmon replica synchronization options that can be selected are listed below. These options can be configured by right clicking a monitored server object and selecting Synchronize Each Directory Partition with All Servers. The synchronization options that users can select are:
- Disable Transitive Replication: This option can be selected to troubleshoot a replication process to a particular domain controller to manually start the replication process.
- Push Mode: When enabled, push mode is enabled for replication and the DRA is no longer enabled to pull updates.
- Cross Site Boundaries: When enabled, start intersite replication for RPC connections only.
How to Start Replication Monitor
Remember to first install Replication Monitor.
- Click Start, Windows Support Tools, and Command Prompt and enter replmon.exe.
- When the Replication Monitor opens, in the console tree, right click Monitored Servers and select Add Monitored Server from the shortcut menu.
- The Add Monitored Server Wizard now starts.
- Select the Add The Server Explicitly By Name option. Click Next.
- In the Add Server To Monitor page, use the Enter The Name Of The Server To Monitor Explicitly box to specify the name of the server that should be monitored.
- Click Finish.
- The server specified for monitoring is now displayed in the console tree.
How to synchronize the Active Directory Directory Partition
Domain controllers that are indicated for a directory partition are regarded as source servers. Source servers can be a Direct Replication Partner, a Transitive Replication Partner, or a Bridge Head Connection.
To synchronize the directory partition:
- Open Replication Monitor.
- Right click the direct replication partner then choose Synchronize Replica from the shortcut menu.
- Replication Monitor now starts the replication process and reports on the status of replication as well.
How to Use the Replication Diagnostics Tool to Monitor/Troubleshoot Active Directory Replication
The Replication Diagnostics Tool (Repadmin) is a command line interface that can be quite useful when troubleshooting Active Directory replication. Through Repadmin, users can perform the following:
- View the replication topology.
- View replication metadata.
- Determine the status/validity of Active Directory information on each domain controller.
- Force replication between domain controllers.
- Manually create the replication topology.
The online help shows the syntax for options and switches of Repadmin. Run repadmin /? for online help. To determine the status of the KCC for replication, run repadmin/kcc. To determine what the replication result was for the last replication process performed, run repadmin/showreps. If running Windows Server 2003, Repadmin offers a few additional functions that can be performed. To view these, run repadmin/experthelp.
How to Configure Active Directory Event Logging
Users can also configure Active Directory event logging. A few key events that can be specified for event logging are listed below:
- Directory access
- Internal configuration
- Internal processing
- Intersite messaging
- KCC
- MAPI events
- Replication events
- Security events
Set one of the following logging levels for an event:
- 0 – None, 1 – Minimal, 2 – Basic, 3 – Extensive, 4 – Verbose, 5 – Internal.
How to Enable Active Directory Event Logging
- Click Start and Run and enter regedit in the Run dialog box. Click OK.
- This opens the Registry Editor.
- Click the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesNTDSDiagnostics registry key.
- The entries that are displayed in the right pane are the types of events that can be logged. The default logging level for each entry is 0 – None.
- Open the entry for each type of event to be logged by double clicking it.
- In each entry’s Value data box, enter the logging level.
- Click OK.
How to Use Dsastat.exe to Monitor/Troubleshoot Active Directory Replication
Use Dsastat.exe to compare the attributes of replicated objects and to determine differences between directory partitions that domain controllers host. Dsastat.exe uses statistics such as objects per server and megabytes per server to determine what the differences are in Active Directory information between domain controllers.
The syntax for Dsastat is:
dsastat [/loglevel:option] [/output:option] [/s:servername[portnumber][;servername[portnumber];…]] [/t:option] [/sort:option] [/p:entrynumber] [/scope:option] [/b:searchpath] [/filter:ldapfilter] [/gcattrs:option[;option;…]] [/u:username] [/pwd:password] [/d:domain]
- /loglevel:option indicates the type of logging. A value of Info, Trace, or Debug can be specified.
- /output:option indicates how results will be displayed. A value of Screen, File, or both of these can be specified.
- /s:servername[portnumber][;servername[portnumber];…]defines the server names that are to be included in the comparison by Dsastat.exe.
- /t:option sets whether a statistics comparison or a full content comparison should be performed. Values that can be set are True for statistics comparison and False for full content comparison.
- /sort:option for setting whether sorted queries should be performed or not. Values are True for sorted queries to be performed and False for specifying that sorted queries should not be performed.
- /p:pagesize specifies the number of entries that should be returned on a page. With a default value of 64, users can specify any value from 1 – 999.
- /scope:option sets what the search should include. Values that can be set are Base, Onelevel, Sub-tree.
- /b:searchpath specifies the distinguished name of the base search path.
- /filter:ldapfilter specifies the LPAD filter that should be used.
- /gcattrs:option[;option;…] indicates what attributes should be returned. Values that can be set are all, LDAPattributes, ObjectClass, auto.
- /u:username sets the username that should be used for the search.
- /pwd:password is the password associated with the above username.
- /d:domain is the domain that should be used to validate the username/password.

kumargoud
thanks bro
regards,
kumar
anuj_85
thanks for the post
regards
Anuj
winservers.co.in