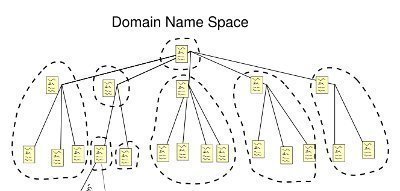
Planning and Implementing a DNS Namespace
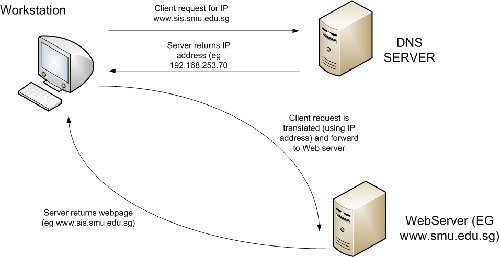
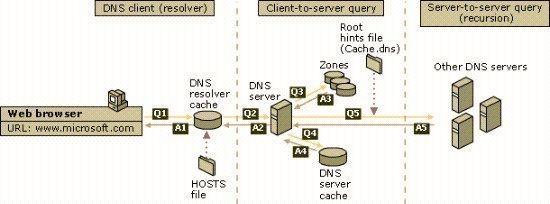
Host Name Resolution Overview In networks running the TCP/IP protocol suite, IP address information is used to forward packet to the destination computer. The packets that are transmitted over the network contain the IP address of the computer sending the packet; and the IP address of the destination computer intended to receive the packet. The …