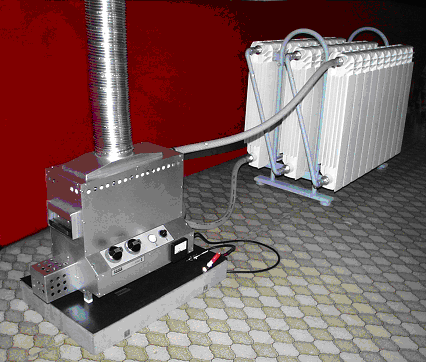
Rectifier
A rectifier changes alternating current into direct current. This process is called rectification. The three main types of rectifier are the half-wave, full-wave, and bridge. A rectifier is the opposite of an inverter, which changes direct current into alternating current. Half-Wave Rectifier The simplest type is the half-wave rectifier, which can be made with just …