Understanding Trust Relationships
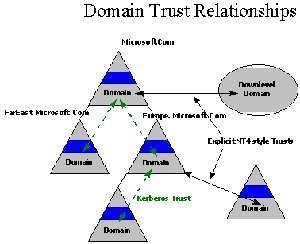
In the Windows NT domain model, domains had to be bound together through trust relationships simply because the SAM databases used in those domains could not be joined. What this meant was that where a domain trusted another Windows NT domain, the members of the domain could access network resources located in the other domain. …