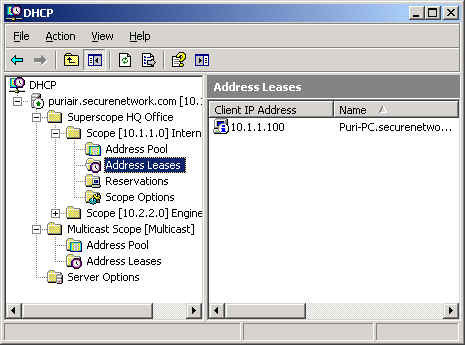
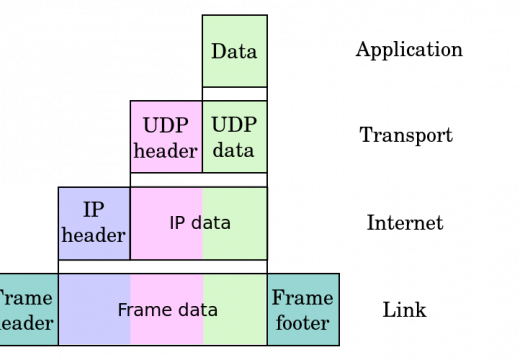
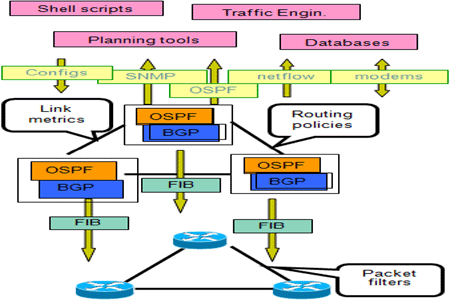
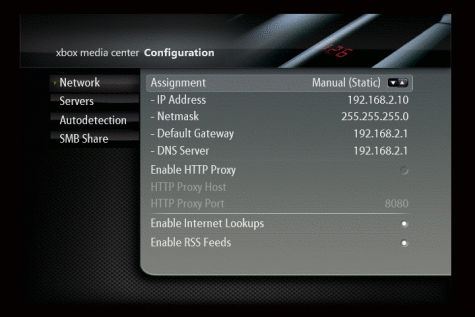
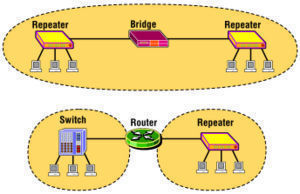
192.168.1.245
Cisco is a leading manufacturer of networking devices such as modems, wireless routers, and network storage devices. Cisco products are sold worldwide to millions of consumers for both residential and commercial purposes. Cisco also markets a number of data plans for some of the largest Internet Service Providers in the world. What is 192.168.1.245? 192.168.1.245 …