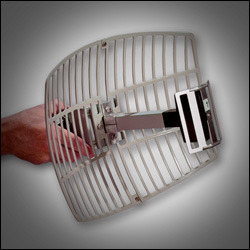
WiFi Antenna
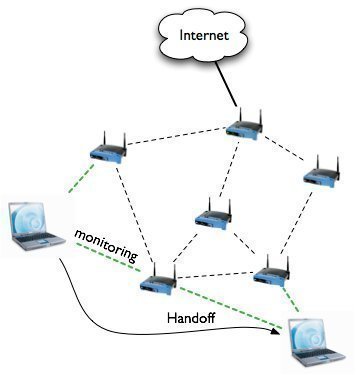
A WiFi antenna is a device that sends and or receives radio signals that computers and other electronic devices use to facilitate wireless communication with each other. While WiFi antennas have many uses, they are most commonly found in or on wireless routers. A wireless router is a device that creates a wireless computer network …