Change TextBox Width with JQuery on Focus and Blur
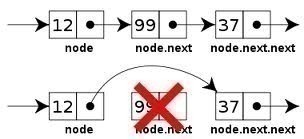
Let’s see how can we change the width of any HTML TextBox using JQuery on occurrence of following 2 actions: Focus and Blur. Focus is when you click anywhere inside a TextBox and Blur is when a TextBox isn’t active or focused. Prerequisite: JQuery Library should already be included in the page. Consider we have …