What is Multicast Wireless?
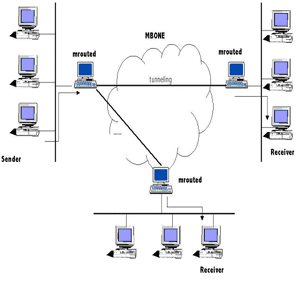
Multicast is the transfer of messages to multiple destinations simultaneously, using fewer networks. The information is delivered to each of the links only once, and copies are created when the links to the destinations split, thus creating an optimal distribution path. Multicasting reduces unnecessary packet duplication. A wireless network utilizes radio communication, unlike wired networks, …