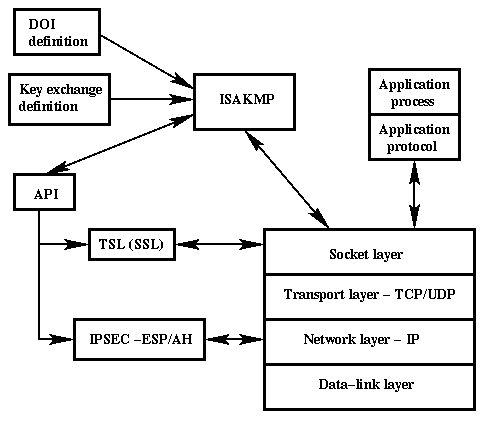
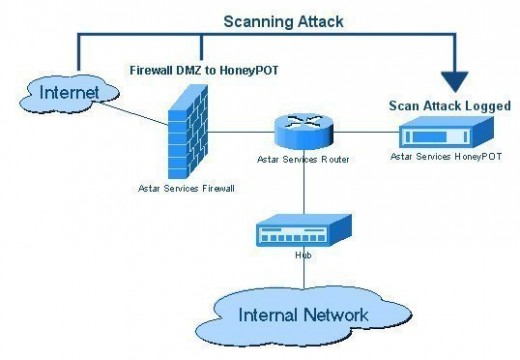
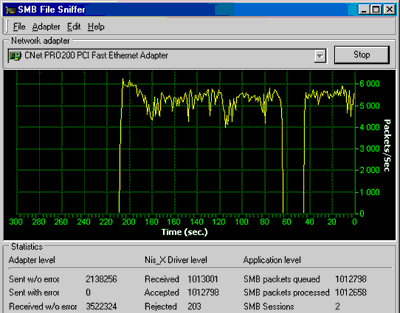
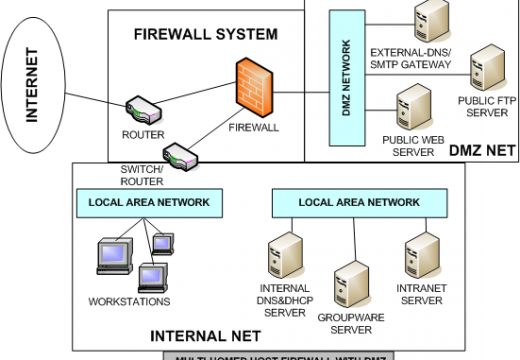
How to Monitor Wireless Traffic
Wireless traffic is considered to be those Internet protocol packets that are transmitted through an 802.11a, b, g, n, or i wireless protocol. Monitoring Requirements There are a few things to consider when planning to setup wireless traffic monitoring. First, the user must determine what kind of traffic will be monitored. Is the traffic to …