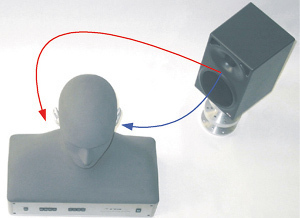
How to Measure Signal Quality
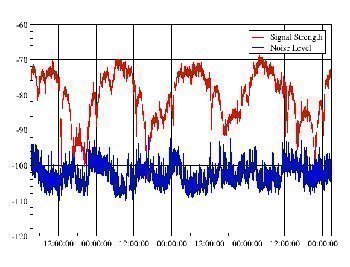
Most people usually look to Signal to Noise Ratio to measure the signal quality of either audio or video communications. Signal to noise ratio is usually written either S/N or SNR. Most of the time the signal to noise ratio is measured in decibels. A decibel is a measure of power or loudness. Not to …