GPG (GNU Privacy Guard)
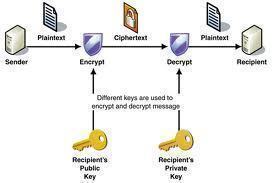
GPG, or GNU Privacy Guard, is a free replacement and competing product for PGP (Pretty Good Privacy). The project is a data encryption and decryption application which provides end-users with a cryptographic privacy and authentication system for communicating electronic data. GPG can be used to sign, encrypt, and decrypt text, for email, files, directories, and …