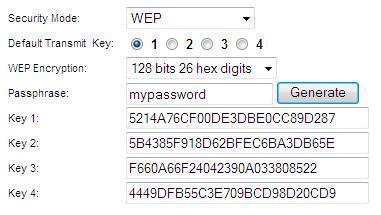
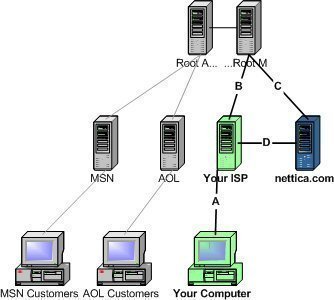
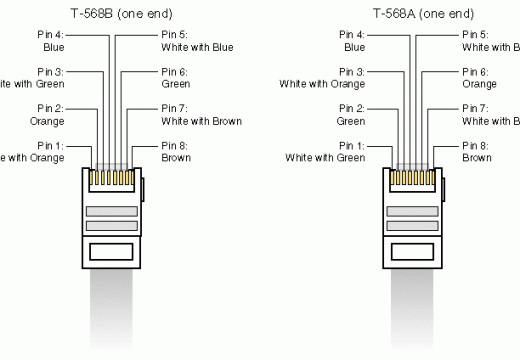
WEP Key Passphrase
A wireless network key is an encryption key for that prevents unauthorized users from accessing a specific wireless network. The user creates wireless network keys, which either a wireless router or a computer that is connected to that wireless router can manage. Wireless network keys can be any length greater than eight characters and can …