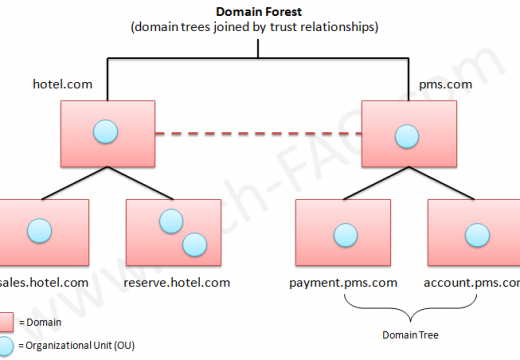
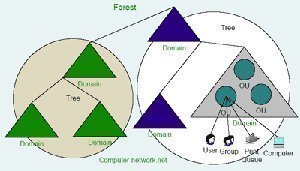
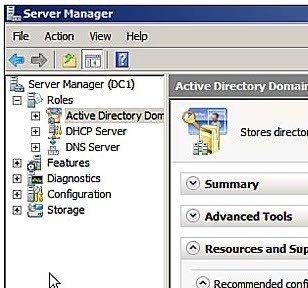
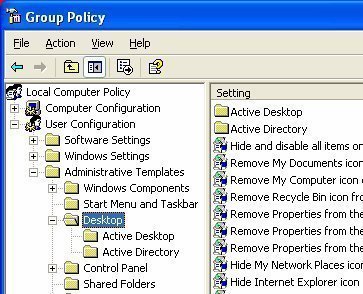
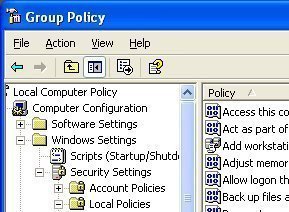
Active Directory Groups
Groups are containers that contain user and computer objects within them as members. When security permissions are set for a group in the Access Control List on a resource, all members of that group receive those permissions. Domain Groups enable centralized administration in a domain. All domain groups are created on a domain controller. In …