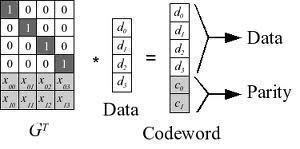
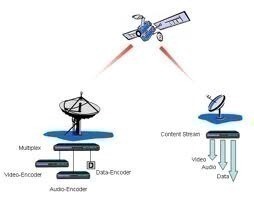
Mobile Satellite Service
Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) is a type of mobile telephone service that depends on portable terrestrial satellites rather than fixed terrestrial satellites that are also known as cell phone towers. Portable terrestrial satellites are similar to cell phone towers, but can be mounted on moving vehicles such as cars, ships, and airplanes, and individual users …