Paraffinum Liquidum
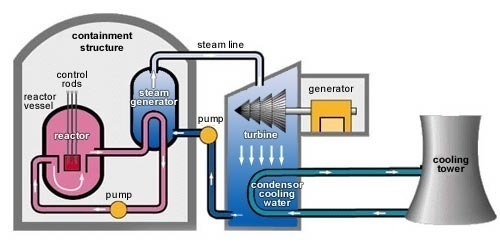
Paraffinum Liquidum (mineral oil) is a petroleum by-product and is created through distillation. Mineral oil is completely transparent and is basically a liquid form of petroleum jelly. It is produced in large quantities and is used in many different ways all over the world, mostly due to its low toxicity and low cost. Mineral oil …